NASA
| National Aeronautics and Space Administration | |
|---|---|
 | |
| NASA insignia Motto: For the Benefit of All[1] | |
| Agency overview | |
| Formed | July 29, 1958 |
| Preceding Agency | NACA (1915–1958)[2] |
| Jurisdiction | United States government |
| Headquarters | Washington, D.C. 38°52′59″N 77°0′59″W |
| Employees | 18,800+[3] |
| Annual budget | US$17.8 billion (FY 2012)[4] See also NASA Budget |
| Agency executives | Charles Bolden, administrator Lori Garver, deputy administrator |
| Website | |
| NASA.gov | |
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics andaerospace research. Since February 2006, NASA's mission statement has been to "pioneer the future in space exploration, scientific discovery and aeronautics research."[5] On September 14, 2011, NASA announced that it had selected the design of a new Space Launch System that it said would take the agency's astronauts farther into space than ever before and provide the cornerstone for future human space exploration efforts by the U.S.[6][7][8]
NASA was established by the National Aeronautics and Space Act on July 29, 1958, replacing its predecessor, the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA). The agency became operational on October 1, 1958.[9][10] U.S. space exploration efforts have since been led by NASA, including the Apollo moon-landing missions, the Skylab space station, and later the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA is supporting the International Space Station and is overseeing the development of the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle and Commercial Crew vehicles. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program (LSP) which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management for unmanned NASA launches.
NASA science is focused on better understanding Earth through the Earth Observing System,[11]advancing heliophysics through the efforts of the Science Mission Directorate's Heliophysics Research Program,[12] exploring bodies throughout the Solar System with advanced robotic missions such as New Horizons,[13] and researching astrophysics topics, such as the Big Bang, through the Great Observatories and associated programs.[14] NASA shares data with various national and international organizations such as from the Greenhouse Gases Observing Satellite.
[edit] Creation
Creation
Main article: The creation of NASA
From 1946, the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics(NACA) had been experimenting with rocket planes such as the supersonic Bell X-1.[15] In the early 1950s, there was challenge to launch an artificial satellite for the International Geophysical Year (1957–58). An effort for this was the American Project Vanguard. After the Soviet launch of the world's first artificial satellite (Sputnik 1) on October 4, 1957, the attention of the United States turned toward its own fledgling space efforts. The U.S. Congress, alarmed by the perceived threat to national security and technological leadership (known as the "Sputnik crisis"), urged immediate and swift action; President Dwight D. Eisenhower and his advisers counseled more deliberate measures. This led to an agreement that a new federal agency mainly based on NACA was needed to conduct all non-military activity in space. The Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) was created in February 1958 to develop space technology for military application.[16]
On July 29, 1958, Eisenhower signed the National Aeronautics and Space Act, establishing NASA. When it began operations on October 1, 1958, NASA absorbed the 46-year-old NACA intact; its 8,000 employees, an annual budget of US$100 million, three major research laboratories (Langley Aeronautical Laboratory, Ames Aeronautical Laboratory, and Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory) and two small test facilities.[17] A NASA seal was approved by President Eisenhower in 1959.[18] Elements of the Army Ballistic Missile Agency and the United States Naval Research Laboratory were incorporated into NASA. A significant contributor to NASA's entry into the Space Race with the Soviet Union was the technology from the German rocket program (led by Wernher von Braun, who was now working for ABMA) which in turn incorporated the technology of American scientist Robert Goddard's earlier works.[19] Earlier research efforts within the U.S. Air Force[17] and many of ARPA's early space programs were also transferred to NASA.[20] In December 1958, NASA gained control of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a contractor facility operated by the California Institute of Technology.[17]
[edit]Space flight programs
Main article: List of NASA missions
The most notable NASA activities are its space flight programs, both manned and unmanned. The latter can be either independent, carrying scientific equipment, or supportive, testing equipment for manned flights. In the beginning, NASA’s missions focused on the spacerace with theSoviet Union, which won the first round, but later USA took the initiative and won the final race to the Moon. The unmanned missions have until now explored most of the solar system. They have also brought telescopes for deep space exploration into orbit around the Earth together with satellites for studying Earth itself.
[edit]Manned programs
The rocket planes experiments started by NACA was taken a step further by NASA which used them as support for spaceflights, the first of which was one-manned and launched by military rockets. When the attention turned to reaching the Moon, the solution chosen was complicated but also the most economical. Supportive projects, both manned and unmanned were introduced and bigger rockets together with spacecraft and moonlander developed. The Moon landing and end of the space race meant a reduction of NASA’s activities. Space stations of a more or less permanent nature, suggested already during the spacerace, were built and an international cooperation was introduced in an attempt to both bring nations together and at the same time share the high costs of space missions. In all, more than 100 manned missions have been made by NASA since 1958.[21]
[edit]X-15 rocket plane (1959–1968)
Main article: X-15
The NACA XS-1 (Bell X-1) was followed by additional experimental vehicles, including the X-15 in cooperation with the US Air Force and US Navy. The design featured a slender fuselage with fairings along the side containing fuel and early computerized control systems.[22] When the spacerace began the main objective was to get a person into space as soon as possible, therefore the simplest spacecraft that could be launched by existing rockets was favored. This led to the choice of a small capsule spacecraft while rocket plane proposals like a modified X-15[23]were turned down.[24] Instead X-15 was used for development of techniques and equipment of value for the space missions. This included jets for changing the orientation of a spacecraft, space suits for astronauts and horizon definition for navigation.[25] Nearly 200 flights were made between 1959 and 1968 allowing NASA to collect data vital not only to the spacerace but also the design of the Space Shuttle.[22] The altitude record for X-15 was 354,200 feet (107.96 km).[25]
[edit]Project Mercury (1959–1963)
Main article: Project Mercury
Project Mercury was initiated in 1958 and started NASA down the path of human space exploration with missions designed to discover if man could survive in space. Representatives from the U.S. Army, Navy, and Air Force were selected to provide assistance to NASA. Pilot selections were facilitated through coordination with U.S. defense research, contracting, and military test pilot programs. On May 5, 1961, astronaut Alan Shepard became the first American in space when he piloted Mercury-Redstone 3, called Freedom 7, on a 15-minute suborbital flight.[27] John Glennbecame the first American to orbit the Earth on February 20, 1962 during the flight ofFriendship 7.[28]
At that time the Soviet Union had taken the lead in the space race. In April 1961, one month before Alan Shepard, cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin became the first person in space when he orbited the Earth once in Vostok 1.[29] Further in August the same year, the follower Vostok 2 made a day long orbital flight[30] which led to canceling of additional American suborbital missions; they were no longer enough.[31] Three more orbital flights were made by the Mercury project after Friendship 7, the last in 1963.[32] Three additional orbital flights were cancelled since it was clear that the Mercury spacecraft had reached its limit of staying in space.[31]
The defeat in the first round of the spacerace led to the introduction of the Moon race program, Apollo, in 1961 just after the flight of Freedom 7. However, it was estimated that this could not be done in one step and that further projects in Earth orbit were needed.[33]
[edit]Project Gemini (1962–1966)
Main article: Project Gemini
Project Gemini focused on conducting experiments and developing and practicing techniques required for lunar missions. The first Gemini flight with astronauts on board, Gemini 3, was flown byGus Grissom and John Young on March 23, 1965.[34] Nine missions followed, showing that long-duration human space flight and rendezvous and docking with another vehicle in space were possible, and gathering medical data on the effects of weightlessness on humans.[35][36] Together with that, Gemini missions also included the first American spacewalks.
[edit]Project Apollo (1961–1972)
Main article: Apollo program
The Apollo program was one of the most expensive American scientific programs ever. It is estimated to have cost $202 billion in present-day US dollars.[37][38] (In comparison, the Manhattan Project cost roughly $25.8 billion, accounting for inflation.)[37][39] It used the Saturn rockets as launch vehicles, which were far bigger than the rockets built for previous projects.[40] The spacecraft was also bigger; it had two main parts, the combined command and service module (CSM) and the lunar landing module (LM). The LM was to be left on the Moon and only the command module (CM) containing the astronauts would eventually return to Earth.
The second manned mission, Apollo 8, brought astronauts for the first time in a flight around the Moon in December 1968.[41] Shortly before, the Soviet had sent an unmanned spacecraft around the Moon.[42] On the next two missions docking maneuvers that were needed for the Moon landing were practiced[43][44] and then finally the Moon landing was made on the Apollo 11mission in July 1969.[45] In 1961 President Kennedy had introduced the Apollo Program and set the deadline for a successful Moon landing at the end of the same decade. It was done by a narrow margin.[46]
The first person to stand on the Moon was Neil Armstrong, who was followed by Buzz Aldrin while Michael Collinsorbited above. Five subsequent Apollo missions also landed astronauts on the Moon, the last in December 1972. Throughout these six Apollo spaceflights, twelve men walked on the Moon. These missions returned a wealth of scientific data and 381.7 kilograms (842 lb) of lunar samples. Topics covered by experiments performed includedsoil mechanics, meteoroids, seismology, heat flow, lunar ranging, magnetic fields, and solar wind.[47] The Moon landing marked the end of the space race and as a gesture, Armstrong mentioned mankind[48] when he stepped down on the Moon.
Apollo set major milestones in human spaceflight. It stands alone in sending manned missions beyond low Earth orbit, and landing humans on another celestial body.[49] Apollo 8 was the first manned spacecraft to orbit another celestial body, while Apollo 17 marked the last moonwalk and the last manned mission beyond low Earth orbit. The program spurred advances in many areas of technology peripheral to rocketry and manned spaceflight, including avionics, telecommunications, and computers. Apollo sparked interest in many fields of engineering and left many physical facilities and machines developed for the program as landmarks. Many objects and artifacts from the program are on display at various locations throughout the world, notably at the Smithsonian's Air and Space Museums.
[edit]Skylab (1965–1979)
Main article: Skylab
Skylab was the United States' first and only independently built space station.[50] Conceived in 1965 as a workshop to be constructed in space from a spent Saturn IB upper stage, the 169,950 lb (77,088 kg) station was constructed on Earth and launched on May 14, 1973 atop the first two stages of a Saturn V, into a 235-nautical-mile (435 km) orbit inclined at 50° to the equator. Damaged during launch by the loss of its thermal protection and one electricity-generating solar panel, it was repaired to functionality by its first crew. It was occupied for a total of 171 days by 3 successive crews in 1973 and 1974.[50] It included a laboratory for studying the effects ofmicrogravity, and a solar observatory.[50] NASA planned to have a Space Shuttle dock with it, and elevate Skylab to a higher safe altitude, but the Shuttle was not ready for flight before Skylab's re-entry on July 11, 1979.[51]
To save cost, NASA used one of the Saturn V rockets originally earmarked for a canceled Apollo mission to launch the Skylab. Apollo spacecraft were used for transporting astronauts to and from the Skylab. Three three-man crews stayed aboard the station for periods of 28, 59, and 84 days. Skylab's habitable volume was 11,290 cubic feet (320 m3), which was 30.7 times bigger than that of the Apollo Command Module.[51]
[edit]Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (1972–1975)
Main article: Apollo-Soyuz Test Project
On May 24, 1972, US President Richard M. Nixon and Soviet Premier Alexei Kosygin signed an agreement calling for a joint manned space mission, and declaring intent for all future international manned spacecraft to be capable of docking with each other.[52] This authorized the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP), involving the rendezvous and docking in Earth orbit of a surplus Apollo Command/Service Module with a Soyuz spacecraft. The mission took place in July 1975. This was the last US manned space flight until the first orbital flight of the Space Shuttle in April 1981.[53]
The mission included both joint and separate scientific experiments, and provided useful engineering experience for future joint US–Russian space flights, such as the Shuttle–Mir Program[54] and the International Space Station.
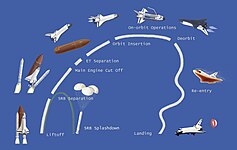
[edit]Space Shuttle program (1972–2011)
Main article: Space Shuttle program
The Space Shuttle became the major focus of NASA in the late 1970s and the 1980s. Planned as a frequently launchable and mostly reusable vehicle, four space shuttle orbiters were built by 1985. The first to launch, Columbia, did so on April 12, 1981,[55] the 20th anniversary of the first space flight by Yuri Gagarin.[56]
Its major components were a spaceplane orbiter with an external fuel tank and two solid fuel launch rockets at its side. The external tank, which was bigger than the spacecraft itself, was the only component that was not reused. The shuttle could orbit in altitudes of 185–643 km (115–400 miles)[57] and carry a maximum payload (to low orbit) of 24,400 kg (54,000 lb).[58] Missions could last from 5 to 17 days and crews could be from 2 to 8 astronauts.[57]
On 20 missions (1983–1998) the Space Shuttle carried Spacelab, a space laboratory designed in cooperation with the ESA. Spacelab was not designed for independent orbital flight, but remained in the Shuttle's cargo bay as the astronauts entered and left it through an airlock.[59] Another famous series of missions were the launch and later successful repair of the Hubble space telescope 1990 and 1993[60]
In 1995 Russian-American interaction resumed with the Shuttle-Mir missions (1995–1998). Once more an American vehicle docked with a Russian craft, this time a full-fledged space station. This cooperation has continued with Russia and the United States as the two of the biggest partners in the largest space station built: theInternational Space Station (ISS). The strength of their cooperation on this project was even more evident when NASA began relying on Russian launch vehicles to service the ISS during the two-year grounding of the shuttle fleet following the 2003 Space Shuttle Columbia disaster.
The Shuttle fleet lost two orbiters and 14 astronauts in two disasters: Challenger in 1986, and Columbia in 2003.[61] While the 1986 loss was mitigated by building the Space Shuttle Endeavour from replacement parts, NASA did not build another orbiter to replace the second loss.[61]NASA's Space Shuttle program had 135 missions when the program ended with the successful landing of the Space Shuttle Atlantis at the Kennedy Space Center on July 21, 2011. The program spanned 30 years with over 300 astronauts sent into space.[62]
[edit]International Space Station (1998–)
Main article: International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) combines the Japanese Kibō laboratory with three space station projects, the Soviet/Russian Mir-2, the American Freedom, and the European Columbus.[63] Budget constraints led to the merger of these projects into a single multi-national program in the early 1990s. The station consists of pressurized modules, external trusses, solar arrays and other components, which have been launched by Russian Proton and Soyuz rockets, and US Space Shuttles.[63] It is currently being assembled in Low Earth Orbit. The on-orbit assembly began in 1998 and the completion of the US Orbital Segment was achieved in 2011. The initial expedition crew size was three, it was decreased to two following the Columbia disaster, since May 2009, expedition crew size has been six crew members.[64]The station can be seen from the Earth with the naked eye and, as of 2012, is the largest artificial satellite in Earth orbit with a mass and volume larger than that of any previous space station.[65]
As mentioned it is a joint project between the five participating space agencies, NASA, the Russian RKA, the Japanese JAXA, the European ESA, and the Canadian CSA.[66][67] The ownership and use of the space station is established in intergovernmental treaties and agreements[68] which divide the station into two areas and allow Russia to retain full ownership of the Russian Orbital Segment (with the exception of Zarya),[69][70] with the US Segment allocated between the other international partners.[68] The station is serviced by Soyuz and Progress spacecraft, the Automated Transfer Vehicle, and the H-II Transfer Vehicle[67] and has been visited by astronauts and cosmonauts from 15 different nations.[71] The Space Shuttle, before its retirement was also used for cargo and crew transfer.
The ISS program is expected to continue until at least 2020 but may be extended until 2028 or possibly beyond that.[72]
[edit]Commercial Resupply Services (2006–)
Main article: Commercial Resupply Services
The development of the Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) vehicles began in 2006 with the purpose of creating American commercially operated uncrewed cargo vehicles to service the ISS.[73] The development of these vehicles was under a fixed price milestone-based program, meaning that each company that received a funded award had have a list of milestones with a dollar value attached to them that they didn't receive until after they had successful completed the milestone.[74] Private companies were also required to have some "skin in the game" which refers raising an unspecified amount of private investment for their proposal.[75]
On December 23, 2008, NASA awarded Commercial Resupply Services contracts to SpaceXand Orbital Sciences Corporation.[76] SpaceX will use its Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon spacecraft.[77] Orbital Sciences will use its Antares rocket and Cygnus spacecraft. The first Dragon resupply mission occurred in May 2012.[78] The first Cygnus resupply mission is expected to occur in late 2012.[79] The CRS program now provides for all America's ISS cargo needs; with the exception of a few vehicle-specific payloads that are delivered on the European ATV and the Japanese HTV.[80]
[edit]Commercial Crew Program (2010–)
Main article: Commercial Crew Development
The Commercial Crew Development (CCDev) program was initiated in 2010 with the purpose of creating American commercially operated crewed spacecraft capable of delivering at least four crew members to the ISS, staying docked for 180 days and then returning them back to Earth.[81][81] Like COTS, CCDev is also a fixed price milestone-based developmental program that requires some private investment.[74]
In 2010, NASA announced the winners of the first phase of the program, a total of $50 million was divided among five American companies to foster research and development into human spaceflight concepts and technologies in the private sector. In 2011, the winners of the second phase of the program were announced, $270 million was divided among four companies.[82] In 2012, the winners of the third phase of the program were announced, NASA provided $1.1 billion divided among three companies to further develop their crew transportation systems.[83] This phase of the CCDev program is expected to last from June 3, 2012 to May 31, 2014.[83] The winners of this latest round were SpaceX's Dragon planned to be launched on a Falcon 9, Boeing's CST-100 planned to be launched on an Atlas V and Sierra Nevada's Dream Chaser, which is also planned to be launched on an Atlas V.[84] NASA wants to have two Commercial Crew vehicles in-service, these spacecraft are expected to begin delivering crew around 2017.[85][86]
[edit]Unmanned programs (1958–)
Main article: Unmanned NASA missions
More than 1,000 unmanned missions have been designed to explore the Earth and the solar system.[87] Besides exploration, communication satellites have also been launched by NASA.[88] The missions have been launched directly from Earth or from orbiting space shuttles, which could either deploy the satellite itself, or with a rocket stage to take it farther.
The first unmanned satellite was Explorer 1, which started as an ABMA/JPL project during the early space race. It was launched in January 1958, two months after Sputnik. At the creation of NASA it was transferred to this agency and still continues to this day. Its missions have been focusing on the Earth and the Sun, measuring magnetic fields and the solar wind, among other aspects.[89] A more recent Earth mission, not related to the Explorer program, was the Hubble Space Telescope, which as mentioned above was brought into orbit in 1990.[90]
The inner Solar System has been made the goal of at least four unmanned programs. The first was Mariner in the 1960s and 70s, which made multiple visits to Venus and Mars and one to Mercury. Probes launched under the Mariner program were also the first to make a planetary flyby (Mariner 2), to take the first pictures from another planet (Mariner 4), the first planetary orbiter (Mariner 9), and the first to make a gravity assist maneuver (Mariner 10). This is a technique where the satellite takes advantage of the gravity and velocity of planets to reach its destination.[91]
The first successful landing on Mars was made by Viking 1 in 1976. Twenty years later a rover was landed on Mars by Mars Pathfinder.[92]
Outside Mars, Jupiter was first visited by Pioneer 10 in 1973. More than 20 years later Galileo sent a probe into the planet's atmosphere, and became the first spacecraft to orbit the planet.[93] Pioneer 11 became the first spacecraft to visit Saturn in 1979, with Voyager 2 making the first (and so far only) visits to Uranus and Neptune in 1986 and 1989, respectively. The first spacecraft to leave the solar system was Pioneer 10 in 1983.[94]For a time it was the most distant spacecraft, but it has since been surpassed by both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2.[95]
Pioneers 10 and 11 and both Voyager probes carry messages from the Earth to extraterrestrial life.[96][97] A problem with deep space travel is communication. For instance, it takes about 3 hours at present for a radio signal to reach the New Horizons spacecraft at a point more than halfway to Pluto.[98] Contact with Pioneer 10 was lost in 2003. Both Voyager probes continue to operate as they explore the outer boundary between the Solar System and interstellar space.[99]
On November 26, 2011, NASA's Mars Science Laboratory mission was successfully launched for Mars.Curiosity successfully landed on Mars on August 6, 2012, and will now begin its search for evidence of past or present life on Mars.[100][101][102]
[edit]Recent and planned activities
NASA's ongoing investigations include in-depth surveys of Mars and Saturn and studies of the Earth and the Sun. Other active spacecraft missions are MESSENGER for Mercury, New Horizons (for Jupiter,Pluto, and beyond), and Dawn for the asteroid belt. NASA continued to support in situ exploration beyond the asteroid belt, including Pioneer and Voyager traverses into the unexplored trans-Pluto region, and Gas Giant orbiters Galileo (1989–2003), Cassini (1997–), and Juno (2011–).
The New Horizons mission to Pluto was launched in 2006 and is currently en-route for a Pluto flyby in 2015. The probe received a gravity assist from Jupiter in February 2007, examining some of Jupiter's inner moons and testing on-board instruments during the flyby. On the horizon of NASA's plans is the MAVEN spacecraft as part of the Mars Scout Program to study the atmosphere of Mars.[103]
On December 4, 2006, NASA announced it was planning a permanent moon base.[104] The goal was to start building the moon base by 2020, and by 2024, have a fully functional base that would allow for crew rotations and in-situ resource utilization. However in 2009, the Augustine Committeefound the program to be on a "unsustainable trajectory."[105] In 2010, President Barack Obama halted existing plans, including the Moon base, and directed a generic focus on manned missions to asteroids and Mars, as well as extending support for the International Space Station.[106]
In September 2011, NASA announced the start of the Space Launch System program to develop a human-rated heavy lift vehicle. The Space Launch System is intended to launch the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle and other elements towards the Moon, near-Earth asteroids, and one dayMars.[107] The Orion MPCV is planned for an unmanned test launch on a Delta IV Heavy rocket around late 2013.[108]
On August 6, 2012, NASA landed the rover Curiosity on Mars. On August 27, 2012, Administrator Charlie Bolden made the first recorded voice broadcast from the surface Mars using Curiosity.
Hello. This is Charlie Bolden, NASA Administrator, speaking to you via the broadcast capabilities of the Curiosity Rover, which is now on the surface of Mars. Since the beginning of time, humankind’s curiosity has led us to constantly seek new life…new possibilities just beyond the horizon. I want to congratulate the men and women of our NASA family as well as our commercial and government partners around the world, for taking us a step beyond to Mars. This is an extraordinary achievement. Landing a rover on Mars is not easy – others have tried – only America has fully succeeded. The investment we are making…the knowledge we hope to gain from our observation and analysis of Gale Crater, will tell us much about the possibility of life on Mars as well as the past and future possibilities for our own planet. Curiosity will bring benefits to Earth and inspire a new generation of scientists and explorers, as it prepares the way for a human mission in the not too distant future. Thank you.[109]
[edit]Scientific research
For technologies funded or otherwise supported by NASA, see NASA spin-off technologies.
[edit]Medicine in space
Main article: Space medicine
A variety of large-scale medical studies are being conducted in space by the National Space Biomedical Research Institute (NSBRI). Prominent among these is the Advanced Diagnostic Ultrasound in Microgravity Study, in which astronauts (including former ISS Commanders Leroy Chiao andGennady Padalka) perform ultrasound scans under the guidance of remote experts to diagnose and potentially treat hundreds of medical conditions in space. Usually there is no physician on board the International Space Station, and diagnosis of medical conditions is challenging. Astronauts are susceptible to a variety of health risks including decompression sickness, barotrauma, immunodeficiencies, loss of bone and muscle, orthostatic intolerance due to volume loss, sleep disturbances, and radiation injury. Ultrasound offers a unique opportunity to monitor these conditions in space. This study's techniques are now being applied to cover professional and Olympic sports injuries as well as ultrasound performed by non-expert operators in populations such as medical and high school students. It is anticipated that remote guided ultrasound will have application on Earth in emergency and rural care situations, where access to a trained physician is often rare.[110][111][112]
[edit]Ozone depletion
In 1975, NASA was directed by legislation to research and monitor the upper atmosphere. This led to Upper Atmosphere Research Program and later the Earth Observing System (EOS) satellites in the 1990s to monitor ozone depletion.[113] The first comprehensive worldwide measurements were obtained in 1978 with the Nimbus 7 satellite and NASA scientists at the Goddard Institute for Space Studies.[114]
[edit]Salt evaporation and energy management
In one of the nation's largest restoration projects, NASA technology helps state and federal government reclaim 15,100 acres (61 km2) of salt evaporation ponds in South San Francisco Bay. Satellite sensors are used by scientists to study the effect of salt evaporation on local ecology.[115]
NASA has started Energy Efficiency and Water Conservation Program as an agency-wide program directed to prevent pollution and reduce energy and water utilization. It helps to ensure that NASA meets its federal stewardship responsibilities for the environment.[116]
[edit]Earth Science
Understanding of natural and human-induced changes on the global environment is the main objective of NASA's Earth Science. NASA currently has more than a dozen Earth science spacecraft/instruments in orbit studying all aspects of the Earth system (oceans, land, atmosphere, biosphere, cyrosphere), with several more planned for launch in the next few years.[117]
NASA is working in cooperation with National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL). The goal is to produce worldwide solar resource maps with great local detail.[118] NASA was also one of the main participants in the evaluation innovative technologies for the clean up of the sources for dense non-aqueous phase liquids (DNAPLs). On April 6, 1999, the agency signed The Memorandum of Agreement (MOA) along with the United States Environmental Protection Agency, DOE, and USAF authorizing all the above organizations to conduct necessary tests at the John F. Kennedy Space center. The main purpose was to evaluate two innovative in-situ remediation technologies, thermal removal and oxidation destruction of DNAPLs.[119] National Space Agency made a partnership with Military Services and Defense Contract Management Agency named the “Joint Group on Pollution Prevention”. The group is working on reduction or elimination of hazardous materials or processes.[120]
On May 8, 2003, Environmental Protection Agency recognized NASA as the first federal agency to directly use landfill gas to produce energy at one of its facilities—the Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland.[121]
[edit]Leadership
Main article: List of NASA Administrators
The administrator is the highest-ranking NASA official and serves as the senior space science adviser to the President of the United States. The administration is located at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC and provides overall guidance and direction to the agency.[122]
The first Administrator was Dr. T. Keith Glennan; during his term he brought together the disparate projects in space development research in the US.[123]
Some administrators like Richard H. Truly (administrator 1989–1992) have been astronauts themselves. Among others he piloted Space Shuttle Columbia in 1981 on its second flight and later supervised the rebuilding of the shuttle program after the disaster of Challenger in 1986[124]
On May 24, 2009, President Obama announced the nomination of Charles Bolden as NASA administrator, and Lori Garveras deputy administrator.[125] Bolden was confirmed by the US Senate on July 15, 2009 as the twelfth administrator of NASA. Lori Garver was confirmed as NASA's deputy administrator.[126]
[edit]Facilities
Main article: NASA facilities
NASA's facilities are research, construction and communication centers to help its missions. Some facilities serve more than one application for historic or administrative reasons. NASA also operates a short-line railroad at the Kennedy Space Center and own special aircraft for instance two Boeing 747 which were used for transport of the Space Shuttle orbiter.
John F. Kennedy Space Center (KSC), is one of the best-known NASA facilities. It has been the launch site for every United States human space flight since 1968. Although such flights are currently on pause, KSC continues to manage and operate unmanned rocket launch facilities for America's civilian space program from three pads at the adjoining Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
Another major facility is Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama at which the Saturn 5 rocket and Skylab were developed.[127] The JPL, mentioned above, was together with ABMA one of the agencies behind Explorer 1, the first American space mission.
[edit]Budget
Main article: Budget of NASA
NASA's budget has generally been approximately 1% of the federal budget from the early 1970s on, but briefly peaked to approximately 3.3% in 1966 during the Apollo program. Recent public perception of the NASA budget has been shown to be significantly different from reality; a 1997 poll indicated that Americans responded on average that 20% of the federal budget went to NASA.[128]























No comments:
Post a Comment
Jayant Parkash Is Welcome All world to my blog